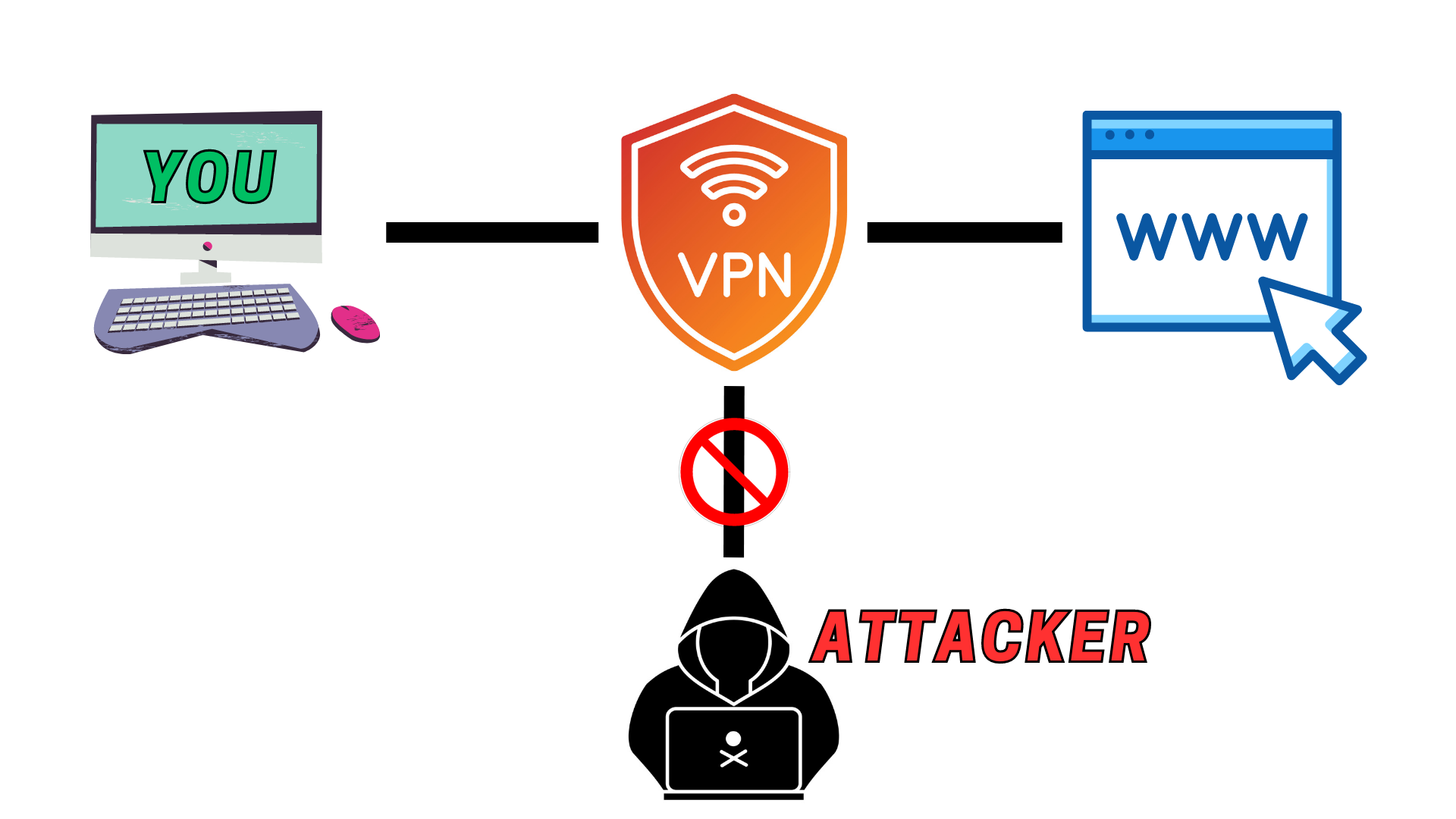
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a service that allows you to create a secure connection to another network over the Internet. It can be used to access region-restricted websites by masking your IP address to appear as if you're browsing from the location of your choice. VPNs are also important for protecting your personal data, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
How Does a VPN Work?
When you connect your computer (or another device, such as a smartphone or tablet) to a VPN, the computer acts as if it’s on the same local network as the VPN. All your network traffic is sent over a secure connection to the VPN. Because your computer behaves as if it’s on the network, this allows you to securely access local network resources even when you’re on the other side of the world. You’ll also be able to use the Internet as if you were present at the VPN’s location, which has some benefits if you’re using public Wi-Fi or want to access geo-blocked websites.
VPN Protocols
VPN protocols determine how data is routed between your device and the VPN server. They are the set of instructions that the VPN uses to handle your data. The most common VPN protocols include:
- OpenVPN: OpenVPN is an open-source VPN protocol that is known for its flexibility and strong security. It uses the OpenSSL library and SSLv3/TLSv1 protocols, along with other technologies, to provide a robust and reliable VPN solution. OpenVPN supports a variety of cryptographic algorithms (e.g., AES, Blowfish), and it is capable of traversing network address translators (NATs) and firewalls. It can run on any port and supports both TCP and UDP transports.
- IPSec: Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a suite of protocols used to secure Internet Protocol (IP) communications by encrypting and authenticating all IP packet transfers. This makes it a popular choice for the remote access VPNs and site-to-site VPNs. IPSec operates at the network layer of the OSI model and can be used to protect data flows between a pair of hosts, between a pair of security gateways, or between a security gateway and a host.
- L2TP: Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a VPN protocol that doesn’t offer any encryption. That is why it is usually implemented with the IPsec encryption suite. L2TP creates a tunnel between two L2TP connection points and IPsec provides encryption for the data flowing through this tunnel. This combination (L2TP/IPsec) provides a robust VPN solution that offers both strong security and performance.
- PPTP: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is one of the oldest VPN protocols still in use today. It was developed by Microsoft and has been a part of the Windows operating system since Windows 95. PPTP is fast and easy to set up, but it is also the least secure of the VPN protocols available today. Its security vulnerabilities have been well-documented over the years, and many VPN providers have dropped support for it.
- SSTP: Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) is a VPN protocol developed by Microsoft. It provides a secure and private connection for internet users and, like OpenVPN, uses SSL/TLS encryption for key exchange. One of the major advantages of SSTP is its ability to traverse firewalls and proxy servers without needing any special configuration. However, because it is proprietary to Microsoft, it is not as widely supported on non-Windows platforms.
VPN Security for Mobile Devices
Mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets are increasingly being targeted by cybercriminals due to the wealth of personal and corporate data they hold. Using a VPN on your mobile device helps to protect your data by encrypting it and routing it through a secure server, making it unreadable to anyone who intercepts it. This is particularly important when using public Wi-Fi networks, which are often unsecured and can be easily exploited by attackers.
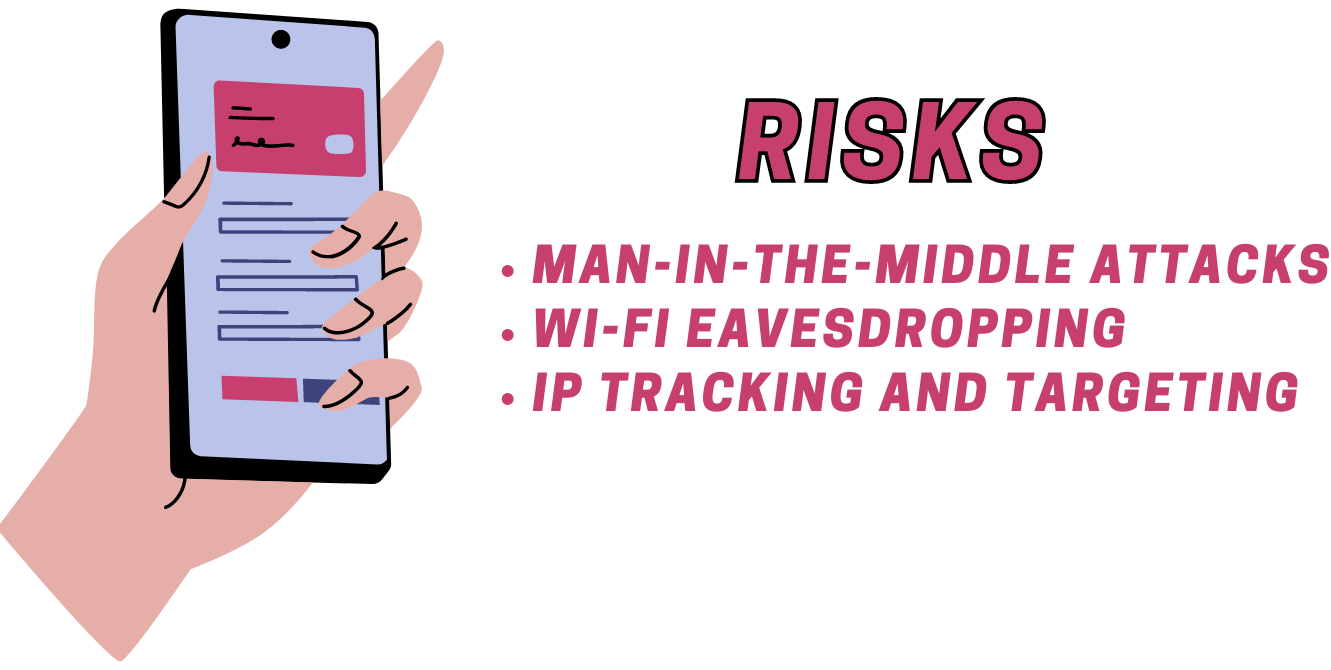
Online Risks:
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: In a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack, the attacker intercepts the communication between your device and the network. They can then steal or manipulate your data. VPNs protect against MitM attacks by encrypting your data, making it unreadable to anyone who intercepts it.
- Wi-Fi Eavesdropping: Public Wi-Fi networks are notoriously insecure. Attackers can easily eavesdrop on your internet activity and steal sensitive data like passwords and credit card numbers. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, preventing anyone else on the network from seeing your activity or stealing your data.
- IP Tracking and Targeting: Without a VPN, websites and online services can track your IP address and use it to build a profile of your online activity. They can then use this profile to target you with ads or even sell it to other companies. A VPN hides your real IP address, protecting your privacy and preventing this kind of tracking and targeting.
Mitigating DNS Hijacking Risk with a VPN
DNS hijacking is a type of malicious attack that redirects you to a different website by altering the DNS server settings on your device. This can lead to serious security risks as you may end up on a phishing site or a site loaded with malware. A VPN can help mitigate the risk of DNS hijacking. Most VPN services run their own DNS servers, preventing your DNS queries from being intercepted. Using a VPN also encrypts your internet traffic and directs it through a secure tunnel, making it difficult for attackers to intercept your DNS queries.
Cloud-Based VPNs
A cloud-based VPN is a form of technology designed to help users access their organization's applications, data, and files through a website or an application. Unlike traditional or static VPNs, a cloud VPN provides a secure connection that can be rapidly deployed globally. Cloud VPNs enable organizations to transition their VPN hosting to the cloud, to improve access to their existing cloud-based resources. They provide globally accessible VPN access to end users and are particularly beneficial for businesses with a remote workforce.
Pros and Cons of Using a VPN
Pros:
- Privacy: Using a VPN hides your IP address and encrypts your data. This not only hides your online activities from your ISP, but also from anyone else who might be snooping.
- Security: A VPN provides a secure tunnel for your data to travel through, protecting it from potential hackers on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Access to geo-restricted content: A VPN can mask your IP address to make it appear as though you're browsing from a different location, allowing you to access content that may be restricted in your current location.
Cons:
- Speed: Using a VPN can slow down your internet speed, as your data has to travel further to reach the VPN server, and it also takes time to encrypt and decrypt the data.
- Compatibility issues: Not all devices are compatible with all VPNs, and some VPNs may not work with all internet services.
- Cost: While there are free VPNs available, they often have data limits, slower speeds, and less reliable connections. For a high-quality VPN, you'll likely need to pay a subscription fee.