Distributed-denial-of-service Attacks
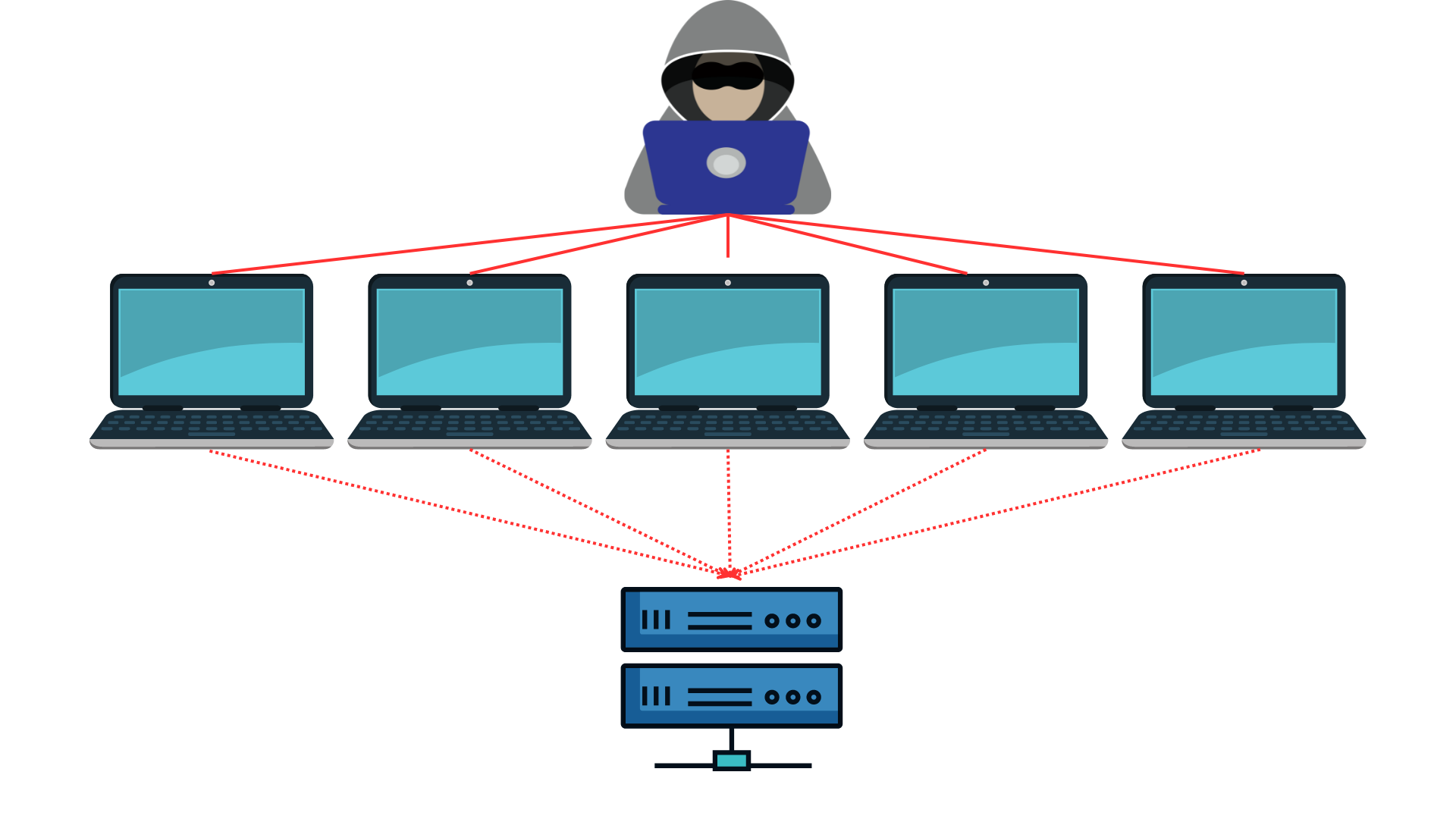
Distributed-denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks are malicious attempts to disrupt the normal functioning of a network, service, or website by overwhelming it with a flood of internet traffic. These attacks leverage multiple compromised devices to launch a coordinated assault, making them more challenging to mitigate than simple DoS attacks.
DDoS Attacks Defined
DDoS attacks aim to exhaust an application's resources by flooding a site with errant traffic. This can result in degraded website functionality or, in extreme cases, taking the site offline. Such attacks are becoming increasingly prevalent and can target various industries, with gaming, ecommerce, and telecommunications being particularly vulnerable. The consequences of a DDoS attack can be severe, potentially compromising a business's online security, sales, and reputation.
How DDoS Attacks Work
During a DDoS attack, a series of bots or botnets inundate a website or service with HTTP requests and traffic. This essentially means multiple computers target a single system, pushing out legitimate users. Service can be delayed or disrupted for extended periods. Moreover, hackers might exploit the chaos to infiltrate databases, accessing sensitive information. DDoS attacks can exploit security vulnerabilities and target any endpoint publicly accessible via the internet. These attacks can last hours or even days, causing multiple disruptions throughout their duration.
Types of DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks can be categorized into three primary types:
- Volumetric Attack: This overwhelms the network layer with seemingly legitimate traffic. An example is the DNS amplification attack, which uses open DNS servers to flood a target with DNS response traffic.
- Protocol Attack: This disrupts service by exploiting a weakness in the layer 3 and layer 4 protocol stack. An example is the SYN attack, which consumes all available server resources.
- Resource Layer Attack: This targets web application packets, disrupting data transmission between hosts. Examples include HTTP protocol violations, SQL injection, and other layer 7 attacks.
Cyber-attackers might deploy one or multiple types of attacks against a network. Some attacks might even evolve or combine with other threats to maximize damage.
How to Detect and Respond to a DDoS Attack
While there's no definitive way to detect a DDoS attack, certain signs can indicate an ongoing assault:
- A sudden surge in web traffic from the same IP address or range.
- Slow or irregular network performance.
- Your website or online service becomes inaccessible.
Modern software solutions can help identify potential threats, and a network security and monitoring service can alert you to system changes. It's crucial to have a DDoS-attack action plan with defined roles and procedures to counter these threats effectively.
How to Prevent DDoS Attacks
Preparedness is key to detecting and remedying an attack promptly. Here are some suggestions for an action plan:
- Develop a DDoS defense strategy.
- Identify security gaps and assess potential threats.
- Update protection software and ensure its functionality.
- Train your team and assign roles for an attack scenario.
Boosting your defense with products, processes, and services can help secure your business. Once a threat is detected, an informed team can act swiftly.
DDoS Protection
Guarding against future attacks requires regular risk analysis, organizing a dedicated DDoS-attack response team, incorporating detection and prevention tools, and evaluating the effectiveness of your defense strategy. DDoS attack protection varies, but with the help of industry-leading experts, you can thwart malicious attacks.
Minimize Your Risk of a DDoS Attack
By securing your platforms, integrating security tools, and enabling rapid response capabilities, you can prevent DDoS attacks across your organization. Cyberthreats like DDoS attacks can harm your online services, affecting functionality, customer trust, and sales. With proper planning, resources, and trusted software, you can minimize your risk.